Starting up a company typically involves several key steps:
- Idea Generation: Entrepreneurs come up with a business idea or identify a problem they want to solve.
- Market Research: They conduct thorough research to understand the market demand, competition, and potential customers for their product or service.
- Business Planning: Entrepreneurs create a business plan outlining their goals, target market, revenue model, and operational strategy.
- Funding: They may seek funding from various sources such as personal savings, friends and family, angel investors, venture capitalists, or through crowdfunding platforms.
- Legal Setup: Entrepreneurs register their company, obtain necessary licenses and permits, and set up legal structures such as partnerships, LLCs, or corporations.
- Product Development: They develop their product or service, often iterating based on feedback from early customers or users.
- Marketing and Sales: Entrepreneurs market their product or service to attract customers and generate sales.
- Scaling: Once the business gains traction, they focus on scaling operations to meet growing demand.
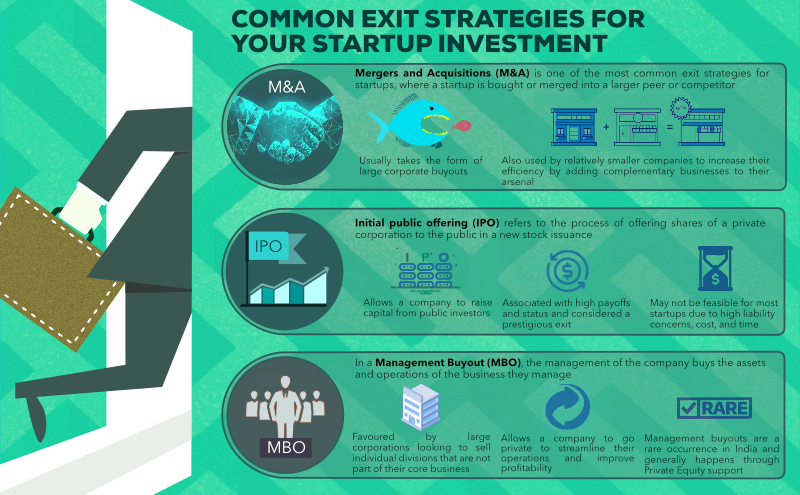
Exiting a company can happen through various means:
- Acquisition: A larger company buys the startup, often to integrate its technology, talent, or customer base into their own operations.
- IPO (Initial Public Offering): The startup goes public by offering shares to the public through a stock exchange, allowing early investors and founders to sell their shares and exit.
- Merger: The startup merges with another company to form a larger entity.
- Management Buyout: The existing management team buys out the ownership stake from investors or founders.
- Shutdown: In some cases, startups may fail to achieve success and are shut down, resulting in the liquidation of assets and closure of operations.
Each path to exit has its own considerations in terms of financial outcomes, impact on employees, and future opportunities for founders and investors.