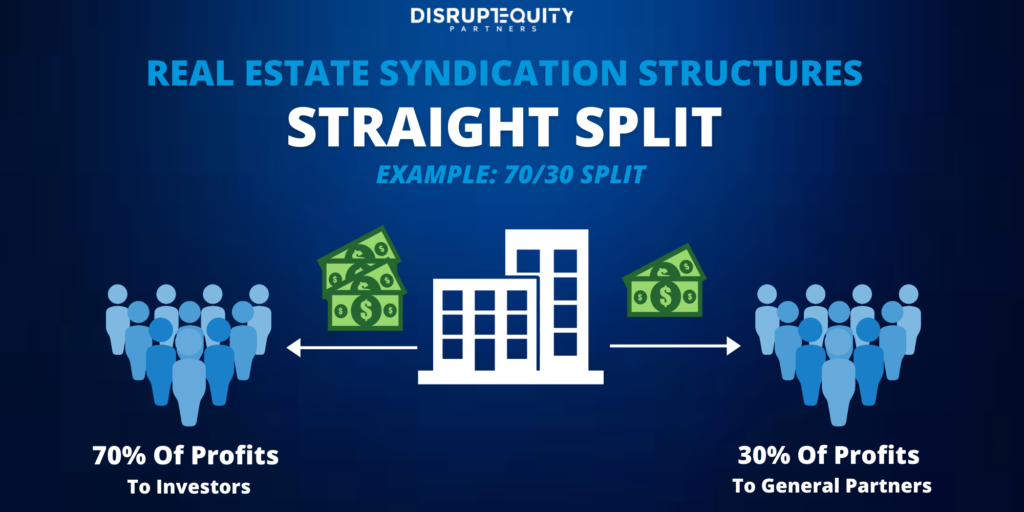
-
Access to Larger Investments: Syndication allows individual investors to participate in larger deals that they might not be able to afford on their own. By pooling resources, investors can collectively access high-value opportunities such as commercial real estate, large-scale development projects, or substantial business acquisitions.
-
Diversification: Syndication provides diversification benefits by spreading investment across multiple projects or assets within a syndicate. Diversifying across various ventures helps mitigate the risk associated with any single investment. For instance, if one property in a real estate syndication performs poorly, the impact on individual investors is minimized due to their exposure to other properties within the syndicate.
-
Expertise and Management: Syndication often involves professional syndicators or sponsors who possess specialized knowledge and experience in the targeted investment area. These experts manage the investment process, from identifying opportunities and conducting due diligence to executing the investment strategy and overseeing ongoing operations. Investors benefit from the expertise of the syndicator, reducing their need for in-depth knowledge or active involvement in the day-to-day management of the investment.
-
Passive Income: Many syndicated investments, such as real estate partnerships or business ventures, generate passive income streams for investors. Income distributions from rental properties, dividends from business profits, or interest payments from debt investments provide investors with regular cash flow without requiring active participation in the operations of the underlying asset.
-
Scale and Efficiency: Syndication enables efficient capital deployment by aggregating funds from multiple investors to pursue larger opportunities. This scale often translates into better negotiation power, access to favorable financing terms, and lower transaction costs. Additionally, syndication structures allow investors to benefit from economies of scale in asset management and operational efficiencies.
-
Risk Mitigation: While all investments carry inherent risks, syndication can help mitigate certain risks through shared responsibility and collective decision-making. In real estate syndication, for example, investors may benefit from shared liability protection, as well as risk-sharing mechanisms embedded within the partnership agreements.
-
Tax Benefits: Syndicated investments may offer tax advantages, such as depreciation deductions, capital gains treatment, or pass-through taxation, depending on the structure of the investment vehicle and the jurisdiction’s tax laws. These tax benefits can enhance the overall returns for investors.
-
Networking and Opportunities: Participating in syndication provides investors with opportunities to network with other like-minded individuals and industry professionals. Through syndication networks, investors can access a broader range of investment opportunities, share insights and experiences, and build relationships that may lead to future collaborations or deals.
However, it’s essential to note that syndicated investments also come with certain considerations and potential drawbacks. These may include reduced control over decision-making, the need to perform thorough due diligence on the syndicator and investment opportunities, the possibility of conflicts of interest, and the potential for illiquidity depending on the investment structure. As with any investment, thorough research and careful consideration of one’s financial goals and risk tolerance are crucial before participating in syndication.